The long-term burden of BMI and cardiometabolic risk factors can cause various health risks in adults. There are researches happening to understand them.
In this article, we will discuss the long-term trends of BMI and cardiometabolic risk factors in adults.
Body Mass Index
The body mass index (BMI) is the metric that is used for determining anthropometric height/weight characteristics in adults. Generally, it is used to classify an index of an individual’s fatness. It is also used for categorising adults in groups.
BMI is also helpful as a risk factor for the development of various health problems. Furthermore, this metric is used while making public health policies.
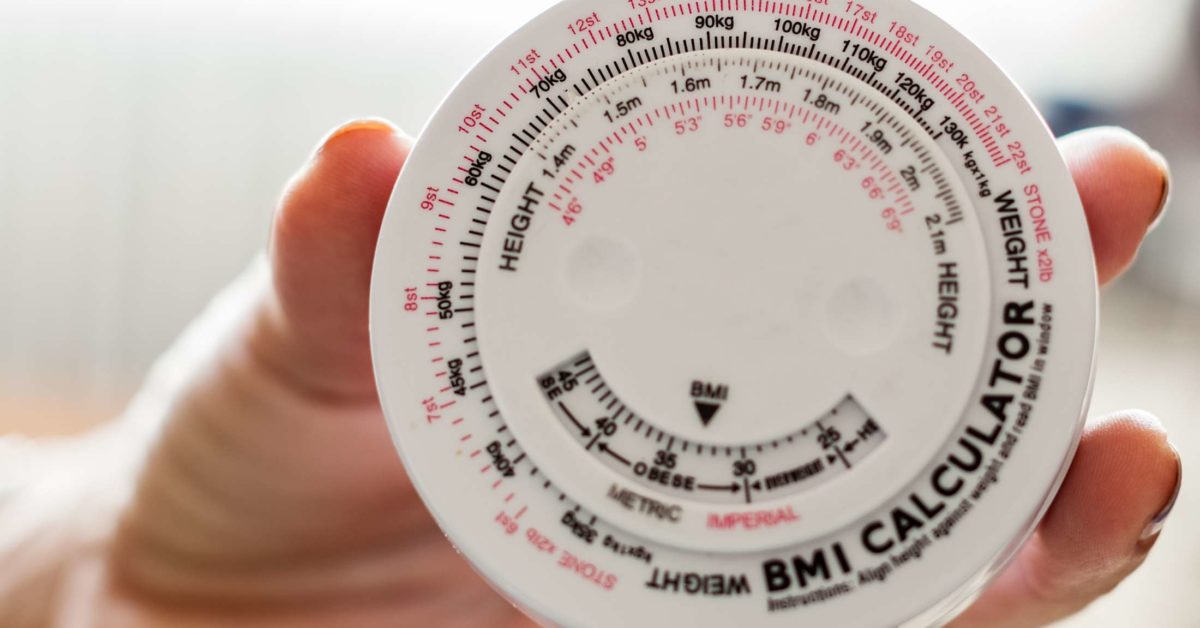
A person can easily calculate his/her BMI using a BMI calculator. He/she will need to know his/her height and weight for the calculation. This metric is an approximate measure of a person’s best weight for height. BMI is calculated by dividing the person’s weight in kgs by his/her height in metres squared.
BMI Classification
A person’s BMI will categorise him/her as underweight, healthy weight, overweight, or obese.
- If BMI is under 18.5
Then the person is considered underweight and possibly malnourished.
- If BMI is between 18.5 to 24.9
Then the person is between a healthy weight range.
- If BMI is between 25.0 to 29.9
Then the person is considered overweight.
- If BMI is over 30
Then the person is considered obese.
Risks of Long-Term Trends of Being Overweight (High BMI)
In case a person is overweight, then he/she might face health problems like-
- Gallbladder Disease
- Cardiovascular Diseases (Heart and Blood Circulation)
- Cancer, such as Breast or Colon Cancer
- Mental Health Problems
Risks of Long-Term Trends of Being Underweight (Low BMI)
If a person is underweight, then he/she might face health problems like-
- Digestive Diseases
- Compromised Immune Function
- Cancer
Cardiometabolic Risk
Cardiometabolic risk informs the likelihood of a person having a cardiovascular situation, such as a stroke or heart attack, in case one or more risk factors are there.
Some of the risk factors are-
- High LDL (Bad) Cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Low HDL (Good) Cholesterol
- Obesity
Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
- To avoid cardiometabolic risk, it isn’t wise for a person to have a BMI considered overweight or obese. It is recommended that a person has BMI between 18.5 and 24.9.
- It is risky to have LDL greater than 100 mg/dl. It is better to have LDL less than 70 mg/dl.
- HDL less than 50 mg/dl in women and HDL less than 40 mg/dl in men can be risky. It is recommended to have HDL greater than 50 mg/dl for women and HDL greater than 40 mg/dl for men.
How Can Cardiometabolic Risk Be Treated?
It is crucial to improve any risk factor if a person wants to lower the cardiovascular risk. For example, people who are overweight or obese can change their exercise, lifestyle, and diet for losing weight. In case a person has one or more than one risk factors, then he/she should consult his/her doctor to understand the cardiometabolic risk and the options to reduce the risk.